-
 观点
观点
HR们常说的胜任力到底是个什么鬼,以及它将如何优化你的招聘技能
来源| 首席招聘官
胜任力的理念最早可以追溯至古罗马时期,那时的人们就构建出胜任力剖面图来描述“一名好的罗马战士”该具有的属性。
管理科学之父泰勒通过“时间-动作”实验发现了优秀工人和一般工人完成工作时的动作差异,被称之为早期的“管理胜任特征运动”。
1973年,美国著名学者麦克利兰(Maclelland)教授为美国甄选外交官设计了一套胜任力指标体系,为胜任力的研究和发展奠定了基础。麦克利兰通过“运用胜任力而不是智力”的研究表明传统运用智力来测量绩效的方式是十分有限的。
经过国内外相关研究的不断变迁与深入,在我国,胜任力呈现出独特的生命力,国内胜任力与绩效关系的特点主要表现在:
第一,用胜任力替代智力来评价绩效得到不断的推广和验证;
第二,胜任力对绩效的影响作用在不同的企业、部门和岗位表现出差异性。
什么是胜任力
这个出生在1917年,美国社会心理学家的“胜任力”理论,让我们的人力资源工作再也轻松不起来,这源于The more you know, the more you don’t know(知道的越多,懂得的越少)。
“胜任力”这个概念最早由哈佛大学教授戴维·麦克利兰(David·McClelland)于1973年正式提出,是指能将某一工作中有卓越成就者与普通者区分开来的个人的深层次特征,它可以是动机、特质、自我形象、态度或价值观、某领域知识、认知或行为技能等任何可以被可靠测量或计数的并且能显著区分优秀与一般绩效的个体特征。
本着系统性、相关性和可操作性的原则,我们认为所谓胜任力,是指在特定工作岗位、组织环境和文化氛围中绩优者所具备的可以客观衡量的个体特征及由此产生的可预测的、指向绩效的行为特征。
从定义中不难分解出,胜任力的核心要素:
针对特定工作岗位的;可客观衡量的;
可预测的;
指向绩效的;
可以说,胜任力模型是最具科学性的人力资源系统性管理工具,没有之一。
读研究生之前,还是招聘小白的时候,给公司招一个市场总监的职位,拿了一份简历给老板,背景、资历、软性的匹配度都不错,老板看了一眼说,这个人不合适,然后就没有然后了。
我当时就纳闷呀,为什么?后来,老板这样给我解释的。
他本科就读于清华大学,院学生会副主席,一定可以去很好的国外高校,但他选择去了南洋理工,一个留学成本低,奖学金高的地方,说明这个候选人的家境一定不富裕;
毕业后先进入了A公司,他在A公司选择的是销售,但大家都知道A公司并不是行业内的顶级公司,只是在区域做的还不错罢了,后面进入了B公司,B是行业内出了名的高工资,但体系和流程这些都不完善,说明这个候选人的求职动机就是薪水;
我们现在需要的候选人是要去搞定渠道关系和媒体关系,需要的是长期稳定的人选,而且在2-3年内薪资不会有显著的变化,他不适合这个职位。
后面我又给候选人打了电话,他家庭为他上学的事情欠了很多钱,还有个弟弟在上大学,他毕业后首先考虑的是把欠款还清并供养弟弟。而且确如老板所说,薪酬在他求职动机里面排第一位的。
这些就因为老板看了一眼简历,都没见这个人(姜还是老的辣)。现在看来,这还只是胜任力模型在领导头脑中的冰山一角,只涉及到了预筛选维度的人口特征和资质一个条件。
其实,胜任能力模型之于招聘,关键在于帮助我们画出人才的脸谱,告诉我们要招聘什么样的人才,什么样的人才更符合我们的企业。
举个栗子:单身狗。
作为“中年妇女”的艾霓姐姐,已经步入了特别热心帮忙介绍对象的年纪,但艾霓姐姐经常遇到一个问题,朋友请帮忙介绍对象,每当问到朋友:“你想要一个什么样的?”的时候,得到的回答经常是:“有眼缘,谈得来就行。”
作为HR的我内心无数头羊驼呼啸而过,眼缘是个什么鬼?谈得来的标准好高行么!我知道你到底喜欢长腿还是大胸,长发姐姐还是短发妹妹?
哎,我就有一个特别要好的朋友,他就很明确的给我说了一二三。我喜欢长的漂亮点的;我希望她有160左右的身高;我虽然是博士但是我不要求她是硕士或者博士,但是怎么也得一个比较好的本科,要不然恐怕沟通有问题……,这条条是道,可量化好评估,活该能快速找到合适的伴侣~
没错,胜任力模型在招聘方向就主要起到这个作用,岗位到底想要什么样的候选人,希望他实现什么绩效,对什么样的人有感觉,给尽量的明确出来。
胜任力模型的确是一个很好用的工具。经过多年招聘实践经验,我曾尝试在招聘的经验中提取有效信息建立我司销售人员素质模型,有成就动机、关系建立、服务意识、信息收集、沟通影响等素质指标。然后我就根据这些素质,结合销售人员具体工作场景,用内隐联结的思路,建立简单易上手的精准推理模型,包括开发面试问题题库,设定观察项与关键行为,通过开放性问题和STAR法,获得对候选人的评估。
什么是内隐联结?
内隐连结可以简单的概括为“条件反射”
看见美食,狗会流哈喇子。
看见钉子,锤子就想往上砸。
看见美女,男性荷尔蒙会飙高。
看见苏格拉底,你就想聊人生哲学。
测验中,在快速反应条件下,被试者对刺激的反应形式是很难有意识控制的,这种情况获得的社会认知结果通常认为是内隐的。
在现实中,大家对胜任力相关知识的学习以及如何构建,又爱又恨,不是没有原因的。因为苍蝇不叮那无缝的蛋,小三不挖那石头墙。胜任力模型是一套准科学的工具,使用和学习的成本都较高,没有点刻苦钻研的学习能力和排山倒海般的好奇心,还真是攻不下这个山头。
相信做HR的,都对胜任力模型和理论有概念和框架,听能听的一直半解,讲也能讲的冰山上下,但要是再往深里面讲,就蒙圈了。
比如在招聘面试中的应用,在培训需求挖掘与人才培养规划中的应用,在人才管理中的分类应用等等,都需要较为专业的人对其进行解读和分析。这也部分说明了,胜任力说起来好听,研究起来很火,但是一谈到实施,就难掩曲高和寡。
今天我们的重点不是精讲胜任力建构,我们主要是讲招聘中的“胜任力”思维。
胜任力思维在招聘中的应用
招聘是个技术活,你既要有人力专业打底,又要辩证认识具体岗位的专业性要求。不懂的人认为人力资源就是招聘,招聘就是问问题,聊聊天,打打分,看着不爽就下一个,聊天谁还不会吖~然后凭感觉用人、留人。但是,作为人力资源部门人员,你若如此行事和思考,那么就Too yang too naïve了。
在我看来,招聘要想实现真正的变化,让自己大有不同,关键是完成视角的转换,否则顶多就是小打小闹庸庸碌碌而已。怎么完成有效的视角转换呢?从本质上说就两条路。
第一条转变,是从由内而外的“个人视角”,转化为由外向内的“他人视角”(岗位视角)。
所谓的“他人视角”就是以岗位分析为核心,真正把岗位性质、价值链条、绩效期待和企业生命周期等串联起来认识一个招聘岗位。这里的重点是,这些个认识,并不是你自己闭门造车的结果,而是经过长期的访谈、调研、分析的结果。
说白了,就是把“胜任力”思维嵌入到你的招聘逻辑中。
实践中,我主要考察如下素质项:
如下是我曾给一个财务主管出的面试意见:
(公司喜欢) 职业岗位技能匹配,账务处理能力丰富。
(同事喜欢) 礼貌谦逊,具备较强上进心与责任心。
(岗位喜欢) 金融行业经验欠缺,但自学信心较足。
(公司喜欢) 生活富足,内心安稳,具有一定持续性。
面试意见切记面面俱到长篇大论,根据公司现阶段和近阶段给出简练且具备逻辑性的简要陈述即可。
可以说,胜任能力模型是招聘的核心指导思想,当你的模型可以被候选人的绩效所验证,才是真正脱离机械性“选角”,真正走向招聘的维多利亚秀场。
关于如何建构胜任力模型,我讲建构三部曲:分析、分解、验证。建构的步骤有很多,但是作为一个懂得化繁为简的职场人,你只要把握好这三个环节就完全够用了,这三点的目标就是明确岗位所需专业技能、分解岗位绩效要求、验证人岗匹配指标有效性。
至于验证环节,你可能会问我,你怎么做信效度的检验?我只能说,这是个不大不小的课题,这主要涉及你的样本空间提取水平与能力,以后我将开辟新的主题来讲讲人力资源中的技术问题。
接下来的工作,招聘反馈与总结,指标修正等工作,相信我不说你也是要一脉相承的要做的。
什么是信度与效度
信度与效度可以简单的概括为“四斤五花肉”
四斤是信度,五花肉是效度。
如果测出来的是三斤或者是三厘米,那就说明信度有问题,信度反应的是测验结果的一致性、稳定性及可靠性。
如果测出来的是里脊肉或者是猪头肉,不是我们想要的五花肉,那就是效度的问题。效度反应的是测量工具或手段能够准确测出所需测量的事物的程度。
第二条转变,是要以未来的视角看问题,要从过去的视角,转化为未来的视角。一句话,要在未来的场景下建立“需要视角”和与之相匹配的评价标准。
举个栗子:就私募基金金融产品经理而言,我们尤其关注候选人的如下素质。
对于私募产品经理而言,产品结构的设计本身并不具备极度复杂性,但一个月薪一万的产品经理和月薪三万的产品经理究竟差距在哪里?
可以说一个有见识的产品经理,一定兼具对产品认识的深度与广度,产品不仅要有好的结构,更要贴合市场。对所有产品要素的认识,我们需要他具备持续学习能力,而这些都不是学校可以教给他们的。
让我们看看如何考察持续学习能力。
我们可以通过四个维度设计问题来考察。一是看志向:关注新知识积极面,看重新知识带给人的收获和未来。二是看自省能力:候选人是否能够客观承认自己在工作中的观点有偏差和错误,并虚心听取意见。三是看好奇心:候选人是否喜欢思考用不同方法让工作更有趣。四是看容错能力:候选人对错误的认知是否是宽容且平衡的。
过多的我不做展开,本篇分享只是在我们的头脑中建立一个有关招聘有关胜任力建构的理论框架。说多了宝宝们都没耐心看也没耐心听,这里面每一个环节都可以作为一个专题再进行拆解,后续也会有相关实用性文章陆陆续续与大家分享。
总之,按照胜任力的理论思想,决定是不是选择一个候选人,不再是“我感觉挺好”、“我认为不行”、“我觉得还可以”等描述性的模糊表述,而是这个候选人的关键指标真正符合具体岗位的胜任能力。这样,符合标准的留下来,有未来发展潜力的留下来,其他,一概断舍离。
是不是觉得自己的逻辑终于有点脉络了?
基于对岗位的深刻认识,再加上持续不断的反馈验证并不断修正,就能让你的招聘技能高出好几个LEVEL!
胜任力模型的构建,只是任职资格体系中一个环节,人才能力标准的认定,人才测评的方式方法等都关乎一个公司的任职资格体系是否完整,这是一个巨大的系统性的工程,非一朝一夕可以完成。
总之的总之,可不要小看了招聘,可别忽视对胜任力的总结与反馈,记住这种思维方式,当你真正能看准人了,除了升职加薪走向职业巅峰,更重要的,你能给自己踏踏实实的选择一个合适的伴侣,那么你才是开始走向人生巅峰了。
-
 观点
观点
全球区块链人才现状:缺口巨大,百万年薪无人能领
文 | 木樨
来源| 一本区块链
“区块链的领先者们,正在竭尽所能争夺行业的顶尖人才。”早在2016年,美国杜克大学福库商学院金融教授Campbell Harvey就这样表示。
领英数据显示,在他说这话的一年之前,全球对于区块链人才的需求量开始猛增,并在2016-2017年经历了爆发式增长。
然而,区块链人才增长的速度,远远赶不上行业发展的速度。
目前,区块链的人才缺口越来越大,国内外都面临着百万年薪无人能领的尴尬局面。
01 全球区块链人才紧缺
IDG Connect在今年5月中旬发布的调查显示,截至2017年,在分布式账本技术创业公司中,至少有115家有近2000个岗位需求。
而国外的大型企业,例如IBM、微软、四大(普华永道、德勤、安永、毕马威)、三星、埃森哲等,已纷纷开始提供区块链相关业务,或着手研发自己的区块链平台。
IDG Connect在调查中还提到,在英国有1000多个区块链招聘信息,而美国则有2000多个。
除了企业方人才需求增加,世界各地的高校也纷纷开设了区块链课程。
据“链塔智库”统计,截至今年4月,美国已有8所高校开设了区块链相关课程,包括斯坦福、麻省理工、普林斯顿等一流大学。
在英国,已有5所大学开设了区块链相关课程,包括牛津、剑桥、伦敦帝国理工等老牌名校。
但缺乏相应师资,却成为高校区块链教育的一大障碍。
纽约大学斯特恩商学院金融系主任David Yermack就曾无奈地透露:“很难找到非常优秀的教师,并将他们留在大学。”
而课程难度过大,是区块链人才培养中的另一大难题。
清华-阿尔山区块链联合研究中心副主任陈文光曾表示,由于清华的分布式课程难度太大,每学期结束,都会有三分之一的学生放弃。
如此大量的人才需求,供给端却显得有些心有余而力不足。主要原因,是掌握区块链相关技术的人才着实稀少。
02 技术类人才需求最大
根据全球自由职业者求职网站Upwork在今年发布的报告统计,2018年第一季度中,掌握区块链技术,成为增速最快的一项技能。
在Upwork上,对于区块链人才的需求,依然是以技术类为主。
熟悉C++、以太坊智能合约、Solidity语言、Python等相关知识的人才,就是各大企业争相抢夺的“种子选手”。
不过,由于区块链是个新兴领域,要想直接找个全能型人才,在当前几乎无法实现。
因此,在人才市场上,不同类型的企业有各自的需求偏好。
有些创业公司只需要应聘者掌握C#编程,之后公司会再花费3-6个月的时间对其进行培训;有些专注于加密货币分析的创业公司,只需要应聘者懂得构建传统的数据库。
实际上,大型的咨询公司也意识到,全能型人才并非是企业的刚需。
这种“大神”都可遇不可求,想要留住他们,企业方还要拿出年薪数百万的诚意。
IDG Connect 的调查还显示,对于拥有企业所需技能的人才,时薪至少100美元;在美国,一个区块链开发人员的年收入中位数是13万美元,远远高于一个其他软件开发人员的平均薪资。
然而,这些人才大多已是身价百万,对财富没那么在意,他们更愿意自主创业、研发项目,而不是为某家公司打工。
03 印度成为人才新战场
印度对于区块链人才的需求与日俱增,成为当前人才抢夺战中强有力的竞争者。
2017年,印度以40%的优势领先于第二名澳大利亚,成为亚太地区最大的区块链人才储备国。中国、新加坡和日本紧随其后,分列三~五名。
根据印度招聘网站Belong的调查显示,印度的班加罗尔、德里、孟买、海德拉巴、浦那、金奈,都是区块链需求重地。
然而,在印度约200万个软件开发人员中,只有0.25%的人才能称得上“区块链人才”。
不过,Belong的联合创始人Rishabh Kaul也表示,印度有10000名开发人员有望在区块链领域谋求一席之地,只要他们有金融科技领域的从业经历。
如此巨大的人才需求缺口,直接推动了印度的区块链课程发展。
在印度,班加罗尔是首个创办区块链学院的邦。之后,喀拉拉邦的印度信息技术及管理研究所与区块链教育网络,共同在喀拉拉邦成立了印度第二个区块链学院,该学院还在今年4月宣布加入了超级账本区块链联盟。
除此之外,印度的安得拉邦政府也宣布和一家新加坡初创公司,以及美国加利福尼亚大学合作,共同建立一所区块链技术学院。
目前,区块链行业巨大的人才缺口,是机遇也是挑战。
没人能准确预测,区块链会何时迎来爆发,何时陷入沉寂,是否会泡沫破灭,是否会再次复苏。
区块链这个新兴行业,确实需要更多的探路者。
-
 观点
观点
谷歌助手问世,预示AI招聘即将成为新趋势?
来源| 环球人力资源智库
AI必定会让一部分员工失业,但人才永远紧缺
近日,谷歌召开一年一度的Google I/O大会。亮出了王牌AIGoogle Assistant,Ta可以无障碍和人沟通,惊艳全场。
发布会上,用户对Google Assistant说:我想剪头发。GoogleAssistant接受指令后直接一个电话轰炸到洗剪吹一把手Tony老师那里!!
Google Assistant:你好,我想帮助我的客户预约做头发。
理发店:预约什么时候呢?
Google Assistant:你觉得3号可以吗?
理发店:我查查Tony老师的档期,请稍等。
Google Assistant:嗯哼?
这一声“嗯哼”把全场人都逗笑了,谁也想不到一个人工智能AI可以做出如此自然的反应…接着,Google Assistant又继续了Ta的表演:
理发店:3号12点不行,Tony老师要帮王阿姨烫头发。
Google Assistant:那10点到12点呢?
理发店:你的客户想剪发还是烫头发?
Google Assistant:就修一下。
理发店:那没问题,我们10点见!
整段对话,Google Assistant表现的自然流畅,理发店那头丝毫没有察觉到自己竟然是在和AI对话。
AI时代已经到来,失业潮也离我们越来越近!商超无人化、配送无人化、公司无人化...的标准场景无人化都将成为未来的目标。
未来的人力资源也将在科技的推动下完成创时代的全新变革,这会让一大批HR被人工智能替代,但这并不意味着所有员工都会失业,因为优秀的人才无论是在过去、现在,还是未来都依然是非常稀缺的。
优秀HR如何识别人才?
寻找「人」而不是某个标签
很多HR寻找人才时首先瞄准TMD、BAT等名企,但HR还是要问问自己,想要的是「人才」还是「某某名企的人」。
也有不少CEO或业务部门负责人偏爱名企出身这个标签,喜欢以公司大小、知名度来衡量和判断候选人的优劣,非BAT,TMD出来的人不看,这是我们经常能够听到。
这样的人才质量真的好吗?真的就能为公司创造价值吗???
如果按照这种逻辑,那就和在菜市场买萝卜没区别了,判断这个萝卜好坏的标准只是通过个够不够大,皮够不够亮,有没有贴着某某牛逼产地标签等等!
HR如果只是这样去招人,不用未来,现在就可以被替代掉。
不是所有的人才都集中在名企和独角兽企业中,招人要有发现人才的独特视角和专业能力,要基于企业的特点、业务需要、用人的要求来思考你所需要的人才到底在哪里,而不是盲目的追求BAT、TMD等名企背景。
「名企出身」是非必要核心条件,是锦上添花、有比没有更好的事情。
所以记住,首先要找的是人才,人才,人才!(重要的事说三遍)
如何甄别与企业匹配的人才?
3+2法则,即3甄2验。
简历甄别, 一份优秀的简历通常呈现出的特点是:内容上逻辑清晰,重点突出,业绩和产出可量化。
面试甄别, 行为+结构化面试,着重了解简历中呈现出的核心内容,及业绩,产出背后的逻辑。
举个例子:
比如XX销售总监在XX知名公司工作期间完成了100个亿的销售任务。
面试官可以从当初的目标设定开始,为什么制定这样的销售业绩目标?
当下的市场环境是怎样的?
竞争对手的同岗位业绩目标设定的范围是怎样的?
实现这个目标所需要的路径是怎样的?
过程中遇到了什么样的问题和困难?
这些问题又是通过什么样的方法解决的?
等等类似的问题去展开面试的甄别。
测试辅助甄别, 基于岗位胜任力模型,了解岗位需求的核心纬度,针对性的给予相应的测试,辅助甄别候选人于岗位的匹配程度。
结合背景调查验证与试用期管理验证综合考察候选人业务能力。
招聘的本质是以需求为导向,需求不仅决定了招什么样的人才,也决定了招聘的路径,什么样的需求匹配什么样的人才,这里面人岗匹配是关键,只有把合适的人放到合适的岗位上才会有最好的效果,岗位上切勿盲目追高追名。
所以无论需要招聘什么样的岗位,前提都必须要搞清楚需求,招聘中遇到的大部分问题都源自于需求本身。基于什么样的背景出现了这样的需求?需求的核心要素是什么?基于核心需求的岗位定位和人才画像是否清晰?根据需求制定有效的招聘计划和策略才是成功招聘到合适人才的基础。
其实,人力资源的工作和医生非常相似。
医生通过望、闻、问、切,找出病人的问题对症解决;HR们通过对组织的望、闻、问、切发现组织上的问题然后通过不同的管理工具解决;而招聘通过筛、甄、测、验招聘到组织中最为合适的人才。
相信短时间内AI还学不会这些非标准化的专业技能, 但我们还是要在AI能够替代我们之前,去提前了解、学习AI,强化工作技能,提升自己的价值,在时代变革的同时完成自我的变革,这才是唯一不被替代的出路。
-
 观点
观点
HR部门:人工智能技术的第一线领域
文| Dr Jeremy Nunn
自古以来,哲学家和科学家们一直在探索人类智慧和思考的奥秘。就像我们在海洋和太空探索一样,我们在知识方面取得巨大进步之后,仍然存在一个萦绕不去的问题:
我们如何运用我们了解到的知识来帮助自己更好地生活和工作?
技术人员凑齐了以人类为原型的人工智能(AI)的最后一块拼图。
人工智能摆脱银幕并进入我们的日常生活,这项技术有望为人类各行各业带来革命性的变化。其中企业家将作为早期的人工智能行业推动者和采用者。
没有比人力资源(HR)部门更好的人机协作场所了。
通过人机协作及其对日常招聘,评估,入职和管理实践的影响,人力资源部门将迎来彻底的转变。
让我们从一开始就明确一件事:AI技术不会让HR经理和员工失去工作。
就像蒸汽机和计算机没有把我们引入过早的反乌托邦一样,AI技术承诺改变人力资源部门,而不是让它们变得多余。
毕竟,它只是许多人力资源专业人员在家中使用的技术的延伸,无论是Cortana,Alexa还是任何其他基于AI的设备。
因此,他们中的大多数人认为人工智能可能为人力资源部门的重要职责带来革命性变化,如招聘,绩效评估和教育,这是一个小小的惊喜。
人才招聘是人力资源部门的主要责任之一,但我们如何确保招聘到的人员是最终需要的“人才”?
假如你最终招到了一位说话流利,看起来很帅的员工,而他很难达到最初的承诺呢?
由于人力资源部门的人群纷杂(也就意味着易受扰乱),他们在这些招聘过程中无法抵抗人类的偏见。
人工智能技术有望通过依靠更多的大数据分析处理,而不是单独的观察来简化这一过程。
对于刚开始使用这项技术的人员来说,人工智能技术在筛选人员时,不受陈旧观念,以及申请人的种族,性别或国籍的影响。
人工智能软件可以设计相关的面试问题,完全忽视某人的背景,专注于他们某项工作的专业能力。
这些评估问题将以申请人早期的工作记录为基础,更重要的是,以他们申请的工作要求为基础。
用谷歌前任HR部门老板的话来说,将AI用于这种类型的自动化可以更快速地过滤出“极好的候选人”。
除了在候选人筛选期间摆脱人为偏见问题之外,人工智能还为人力资源部门提供了很多其他帮助,从而减轻了筛选候选人简历,社交媒体帐户,参考信函和其他来源的千兆字节数据的巨大负担。
这个过程是人力资源专业人员面临的最耗时的任务之一,他们往往面临为了及时完成工作而需要削减一些候选人的问题。
这无意中造成了公司招聘程序的缺陷,并可能把错误的人放在公司的错误位置。
最后,这也需要重复地耗费时间和昂贵的重新招聘程序。
人工智能可以使这些繁琐过程成为企业HR实践历史的一部分。
这归功于其强大的分析能力,使得人工智能可以同时处理大量候选人的大量数据。
如果可以的话,这些信息不必停留在简历或参考资料中,但也可以包括招聘后的绩效评估,这些评估为申请人的潜力提供了宝贵的见解。
人工智能处理这些任务所节省的时间可以在几天甚至几个月内进行衡量,人力资源专业人员可以将其用于实时访谈,入围和业绩分析。
AI通过协助新员工提供入职手续,再次释放HR部门资源。
这些新进人才经常淹没于人力资源部门,处理许多与薪资支付,假期,福利和一般权利有关的问题。
对HR专业人员来说,回答公司在宗教节日期间缺勤或未付奖金的政策等问题既重复又耗时,而人工智能可以使用日益智能的聊天机器人来“解救”这些人员。
他们可以很容易地编程,实时提供日常问题的答案,无论新员工或老员工的问题。
这些机器人可以作为自助服务平台,让人力资源人员能够专注于回应更加复杂和迫切的问题,那些更应该引起注意的问题。
最后,人工智能可以提供HR管理方面的协助,比如协助现有员工绩效评估的进行。
监控绩效会产生大量的各种数据和指标,人工智能可以对这些数据和指标进行梳理,以便人力资源经理能够快速访问有价值的系统化见解。
这些指标可以根据AI设计的每个员工的绩效目标进行衡量,也可以包括行为评估。
人工智能可以帮助人力资源人员为每位员工设置分级系统,并对设定的绩效目标进行定期自动化审查。
在企业界,人工智能最佳使用领域之一是人力资源部门,作为公司处理“人”的业务的第一线。
在人工智能领域,他们可以在其专业工作的各个阶段找到一个伟大的盟友,从早期入选人才和申请人筛选到后期上岗程序和绩效评估。
除了消除人力资源人员不必要的负担之外,人工智能可以帮助简化所有这些任务,并对每位候选人和员工的真实潜在业绩产生前所未有的见解。
所有这些都是在没有人为偏差和错误能力的限制的情况下完成的,这使得AI成为未来成熟的人力资源管理工具。
-
 观点
观点
名企都在用的5种HR数据分析
文| bernard marr
HR数据提供了一种方式,使我们可以做出更好的与人相关的决策,更深入地了解员工的感受,并提高绩效。
让我们看看人力资源团队通过数据分析增加价值的一些出于意料的方式。
寻找令人兴奋的新招聘渠道
我最喜欢的例子之一来自沃尔玛对数据分析师的创造性搜索。他们不是通过传统渠道进行广告宣传,而是在Kaggle上提出挑战。
Kaggle是一个众包的分析竞赛平台,“扶手椅数据科学家”将其技能应用于公司提交的任何分析问题。那些在沃尔玛的数据挑战中表现出色的人在该公司获得了一份工作。
根据沃尔玛技术部门的高级招聘人员Mandar Thakur表示,由于这次挑战,有几个人被聘请加入沃尔玛分析团队,其中包括沃尔玛技术部。如果根据他们的简历,招聘部门则根本不会考虑采用他们。
在赛车运动的世界里,日产也通过一个不寻常的渠道招募:赛车视频游戏!日产与索尼合作创建GT Academy,这是一项全球性年度比赛,旨在发现最佳游戏车手,并将其变为真实的赛车手。每年都有数十万的人希望参加比赛。
所有在过去几年中脱颖而出的获胜者仍然在比赛,这证明了日产的这种招聘渠道是有益的。
人力资源团队的外包:不要等待最好的人才主动敲门。找出你理想的人才留在哪里,并将你的招聘工作集中在那里。
参与和激励员工
行为分析公司Humanyze提供的电子徽章可以捕捉员工对话中的信息,包括对话的长度,涉及的语气,人们打断的频率,表达移情的程度等等。
一家大银行利用这项技术注意到,其表现最出色的呼叫中心工作人员是那些一起休息并集体放风的人。
基于这些知识,银行实施了群体休息政策。结果?员工的绩效提高了23%,压力水平下降了19%。
此外,IBM使用情绪分析来收集员工帖子在其内部社交网络平台上的见解。
例如,当IBM正在检修其绩效审核系统时,该公司转向内部网络,要求员工对新审核系统的想法提出反馈意见。他们收到了数以万计的回应。
使用Social Pulse文本分析软件,IBM表现出一种普遍的担忧:员工不喜欢他们的日常表现被曲线分级。
得益于数据和分析,公司能够及时采取行动,并在绩效评估中对此方法进行折扣。
提高员工的安全和福利
钢铁生产商North Star BlueScope Steel一直与IBM合作设计一项安全计划,该计划将IBM Watson的认知计算能力和传感器整合到腕带和头盔中。
这个名为IBM Employee Wellness and Safety Solution的项目实时向工人和主管提供安全警报。例如,如果技术检测到工人没有移动,并且他们的心率和高温增加,这可能意味着他们正在遭受劳累或者甚至是极度高温的压力。
在这种情况下,可以提醒主管,或者建议员工休息一下。
在另一个例子中,澳大利亚Seeing Machines公司开发了采矿卡车技术,跟踪驾驶员的眼睛,以便发现驾驶员的疲劳。
该系统使用摄像头,GPS和加速计来跟踪眼睛和眼睑的运动,例如司机眨眼多久,眨眼持续多久以及眼睑移动速度有多慢 - 即使司机穿着它也可以做到这一切墨镜。当驾驶员闭上眼睛的时间超过1.6秒时,卡车内会发出警报 - 座椅内部产生噪音和振动。
然后,如果再次触发警报,则会通知调度员或主管,以便他们可以通过无线电与司机联系。
人力资源团队的收获:技术,特别是传感器,已经帮助工作场所更安全了很长一段时间 - 想想烟雾报警器,安全和进入系统等 。
但现在,由于大数据和分析,公司能够将员工安全提升到一个全新的水平。
使学习和发展更有效
随着在线学习的兴起,针对个人学习者,企业学习和发展日益变得个性化。在数据和分析的推动下,“适应性”学习技术允许对课程细分,以及对活动和试题进行个性化定制,以适应学习者的偏好,学习速度和最佳学习方式。
个人在线自学也可以说比将员工从工作中抽出一天或一周时间带到昂贵的培训课程上更具成本效益。重要的是,像这样的自我导向学习有助于将持续发展融入员工日常生活中。
达能的在线达能校园2.0就是其中一个例子。这家食品巨头创建了一个用户友好的在线平台,员工可以通过这个平台促进他们的发展并与其他员工分享最佳实践和知识。
人力资源团队的外包:
这一数据驱动的人力资源领域可能不如其他领域发达。但即使只是对目前学校数字化转型的一瞥,大学和高校也指出数据如何以令人兴奋的新方式促进企业学习和发展。
驾驶表现......不疏远人
UPS已经将性能管理中的数据和分析应用到了一个全新的水平。例如,司机携带多年的手持式计算机(你签收的那些智能储物柜告诉你收到了你的包裹)实际上是一种复杂的设备,可以帮助司机做出更好的决定。
例如,哪种订单能够以最高效率递送包裹路线。此外,UPS卡车配备了200多个传感器,用于收集数据,包括驾驶员是否系安全带,驾驶员有多少次需要倒车或掉头。
通过监测驾驶员并在需要时向他们提供反馈和培训,UPS每年减少850万加仑燃料和8500万英里。另外,司机现在每天平均停靠120次。这个数字以前不到100--这意味着使用相同卡车的相同司机现在可以提供比以前更多的包裹。
你会认为如此紧密的监控员工可能会引起员工之间的冲突。但增强的性能意味着该公司可以向其司机支付业内最高的工资,这无疑有助于支持员工购买数据驱动的绩效。该公司还采取了其他措施,以确保他们不会面临司机的反弹;
例如,根据驾驶员合同的条款,UPS不能在没有通知驾驶员他们正在收集什么的情况下收集数据。他们也不能仅仅根据数据告诉他们的信息来对驾驶员进行管理。
人力资源团队的外包:
数据驱动的人力资源可以让企业摆脱传统的,耗时的绩效管理方法,例如年度绩效评估(一般对管理人员和员工都感到恐惧)。
现在,我们可以更经常地(甚至实时)更好地监控实际绩效,并以更具建设性,持续和一致的方式向员工提供反馈意见。
-
 观点
观点
改善员工体验的三大策略:创造属于你自己的雇主品牌故事
文| dave sutton
2016年底,Asurion的人才招聘与保留团队意识到,如果他们想赢得顶尖人才,他们需要改善员工体验(EX)。
这家私营公司为3亿多客户提供移动设备保护和技术保修服务。他们帮助人们保持在线并实现最佳生产力。
这意味着这家公司需要大量的技术人才!
在科技领域,人才争夺战是真实存在的。我们正在经历很长一段严峻的人才短缺时间。
“雇用时间”的数量似乎永无止境,68%的人力资源经理表示他们在填补职位方面遇到困难。招聘经理在一个非常有限的人才库中对合适人选的竞争是非常激烈的。
Asurion需要讲述一个清楚而真实的雇主品牌故事,说明为什么一个技术人员应该加入,以及为什么现在的高绩效员工应该留在公司工作。
Asurion的领导层依靠David Marks创造了一个引人注目的雇主故事,完全使EX从“同一片海中脱颖而出”,并使公司与市场上的竞争雇主脱颖而出。
大卫需要有效地传达Asurion的雇主品牌故事以达到他们所追求的高品质人才,并确保EX完全符合他们故事的承诺。
你可能会认为薪酬是引人注目的员工体验的关键。但是,正如David在Asurion学到的那样,提高工资可能是员工头脑中的首要问题,但薪酬通常远远低于实际触发加入或留在组织中的行为的收益。
事实证明,许多改进EX的策略都非常具有成本效益,并且更易于实施和维护。
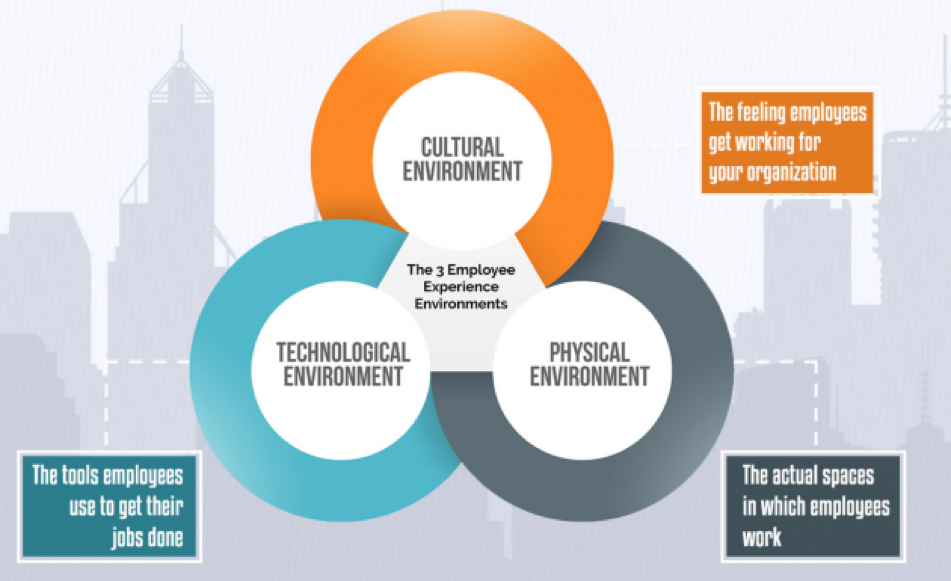
正如Jacob Morgan在他的书“员工体验优势”中指出的那样,有三种环境构成了任何员工体验:文化,技术和物质。
文化环境体现了员工为公司工作的感觉。
技术涵盖了员工用于完成工作的工具和功能。
身体体现了员工工作的实际空间。
图形信用:员工体验优势
这三种环境相互支持和加强。一些最有趣的策略实际上存在于上图中的交叉点处。
这里有三个策略来塑造员工对环境的看法并提高员工体验:
1.提供时间表和工作场所的灵活性
你的员工比你更了解他们的工作日要领。即使你是一个超级微管理人员,你可能不会每天与你的每一位客户打交道。
你的一线员工是你业务的一面。如果你赋予他们自主决策权并让他们负责管理自己的工作量并获得结果,那么他们对EX的看法就会大大改善。采用弹性工作时间和远程办公的工作场所在EX上得分更高。
如果你可以帮助员工避免每天繁忙的通勤时间,你也会看到生产力的提高。在Asurion,可定制的时间表选项对于未来的员工来说是一大吸引力,随着员工对工作生活的更多控制,它增加了整个业务的积极性和动力。
2.制定战略性员工投资
虽然很容易假设大多数人只为薪水工作,但高绩效员工正在越来越多地寻找更多追求。
终身就业的日子已经过去了,但这并不意味着你不应该培养能够强化个人和职业发展的员工体验。
Asurion公司最具潜力的员工将他们的工作视为在科技行业内学习,成长和进步的机会。
创造学习型文化和投资于员工职业发展的好处是广泛而令人鼓舞的。
当员工知道他们正朝着个人目标迈进时,他们的积极性和积极性就会增加,并减少任何停滞和无聊的可能性。
庆祝和欣赏你的团队的成就,他们会在绩效和倡导方面为你带来10倍的报酬。
3.确保简单明确的角色和责任
没有什么比开始一项需要新职能的新工作更糟糕,你实际上被要求扮演与之前完全不同的角色。
Asurion竞争的信息技术领域尤其如此。
“技术”是一门广泛的学科,很难找到同时擅长多种IT功能的员工。
有时候,最好的策略是以不同的方式思考问题,并在EX中包含人员配备能力。
利用领先IT专家的按需工作人员,你可以在IT功能的某些部分填写特定角色和特殊技能组。
这可以让你的内部员工将精力集中在更具战略性的挑战上,同时为员工对其角色和工作量的感知带来更多的简单性和清晰性。
与客户体验(CX)非常相似,有吸引力的员工体验(EX)为你的目标受众提供了关心理由,听取理由,参与理由,加入理由以及最重要的理由。
通过将文化,技术和物理环境与你的雇主品牌故事结合起来,你可以吸引并留住高绩效团队。
以上内容由HRTech AI编译完成,仅供参考e
-
 观点
观点
区块链离我们很远吗?已经有人将它用到HR工作中去了!
来源| 中国人力资源
今年区块链大火,区块链的应用已经从我们熟知的金融行业应用延伸到经济社会的各个领域里,也已经有人将区块链技术运用到了人力资源管理领域,用科技解放HR。
如果你还不清楚区块链是什么?
区块链是一种去中心化的,基于密码学和公式机制的分布式账本技术,特点是去中心化、可追溯、防篡改,每个数据节点都记录了全量数据。
在区块链网络里,不存在一个中心化节点,每个数据都在整个网络里等价存在,而且相互之间通过链式关系进行关联,每一个区块和前一个区块按照链式关系相连,构成一个长链,所以叫做区块链。
区块链的主要优势是无需中介参与、过程高效透明且成本很低,数据高度安全。
区块链怎么用在人力资源领域?
简历“溯源”
目前这个阶段,“追本溯源”是“可信”的区块链最集中的应用。区块链技术决定它不能篡改,它提供给消费者的信息就更容易得到信任。
据悉,目前众安集团在400多个养鸡场使用了区块链技术,“在鸡脚上装上识别器,消费者可以直接查询这只鸡过去的饲养情况,甚至可以知道它走过多少步,是不是一只爱运动的鸡。
浪潮集团也在应用区块链技术建设“中国质量链”,并且已经开始在为包括茅台在内的多家企业提供服务,核心就是用区块链解决产品溯源问题,比如说一瓶茅台,可以从生产环节、流通环节、第三方检测3方面对这个产品进行追踪,对产品全生命周期数据进行串联,为消费者提供产品溯源和鉴真服务。
而区块链“溯源”用在HR领域也帮助HR解决了员工背景真实可靠度的问题。
简历欺诈是人力资源领域的一大难题。事实上,一个最大的在线求职网站CareerBuilder的调查显示,大约58%的雇主在简历上发现了谎言。
雇主如何确定一个理想的候选人对他们的资历和经历诚实呢?
区块链可以对简历进行加密与智能认证,确保应聘者的简历中教育经历、工作经历等的真实性,实现应聘方简历信息的真实性、不可篡改性、不可伪造性,解决了困扰网络在线招聘多年的招聘信息失真这一问题。
现在有许多初创公司正在探索区块链技术解决认证问题的能力,增加透明度并解决简历欺诈问题。
在区块链的帮助下,HR可以通过验证其证书来为自己的业务寻找合适的人员。如果你想确保一个人确实有符合公司要求的资质,那么区块链可以提供帮助。
而且,这一切不再只是幻想,Blockcerts就运用区块链技术,就可以实现查看员工的真实背景,了解你要的人是否具备其所说的资质。
区块链技术还可以帮助人们验证身份。当数字身份和认证记录结合起来时,你就能轻易迅速地找到许多候选者。
大学还可以采用区块链追踪成绩单和课程。通过这种方式,可以看到候选人是否拥有可以在业务中发挥作用的其他经验或知识,即便其能力认证可能并不完全符合职位要求。申请人可以选择分享其证书,这样雇主就可以使用应用程序来验证并检查这些信息。
在国内,职业链(CTEChain)与腾讯进行了合作,主要研究人力资源和区块链技术两个主要领域,最终目的是建立一个能够降低风险和提高招聘效率的职业信用生态平台。通过腾讯的大数据优势与科技优势,在企业招聘、员工内部管理系统、风险管理体系建设、招聘效率提升等方面进行深度合作,助力企业更好发展。
Aworker也利用区块链技术,让求职者能够将他们的简历存储在区块链中,立即证明其资历的公司。
作为分散评估和验证的结果,候选人简历的详细信息会实时更新。由于区块链上的数据是透明的,并且没有人可以根据自己的利益操纵数据,所以不存在伪造或欺诈行为。
不仅如此,使用区块链技术可能使人们更容易地获取公共信息。使用区块链技术可以安全地进行背景调查,查看犯罪记录或其他公共信息。
雇佣关系
在移动互联网的推动下,共享经济已经不再是一个新鲜事物,共享单车、共享雨伞、共享酒店纷纷出现。
在共享经济的背景下,越来越多的年轻人可能不再隶属于任何一家公司了,他们不再以自己是大公司的员工为荣,而是沉浸于自己在哪个平台上创业,乐于更广泛的合作。
对于企业而言,企业和员工之间原有雇佣关系将会被削弱,不再是雇佣关系下的正式员工,而是企业在某个固定领域的合作伙伴。
领英的创始人曾经提出,“商业世界需要有利于相互信任、相互投资,共同受益的新雇佣关系框架。理想的雇佣关系框架应鼓励员工发展个人人脉、勇于开拓实干,而不是成为唯利是图的跳槽专业户。”
利用区块链技术,可以让全世界各地的人通过去中心化的全球网络,交易他们的时间和才能,实现“共享员工”。
澳大利亚的技术公司ChronoBank通过利用区块链,可以让全世界各地的人通过去中心化的全球网络,交易他们的时间和各自的才能。
ChronoBank.io短期工作招聘平台是ChronoBank开发的区块链人力资源项目,其目标是建立一个去中心化的全球时间银行网络,让工作者可以在其中自由交易他们的时间和才能,而且无需传统金融系统的介入。目前该项目主要关注短期人力资源领域,包括电子商务、清洁、仓储、工业、建筑等自由职业。
基于区块链的自由职业劳动力招聘平台,将时间作为货币,ChronoBank能够确保人们根据自己的努力而获得报酬、提供了基于以太坊和其它区块链的最可持续的稳定代币。Chronobank使用有信誉的大型人力资源企业来确保所发行的劳动力时间(LH)代币的供应,本质上创建了一种传统银行的替代方案,更加低廉和透明。
培训
利用区块链技术,有望打破员工在各个公司任职时的培训壁垒,形成一个基于区块链技术的分布式账本,用于存储学习者在各个不同的公司的学习记录,从而建立起即时更新的、不可篡改的学习培训经历,形成员工学习进步的记录。
区块链技术可以优化和重塑网络学习社区生态, 使用虚拟币提高社区成员参与度,形成社区智慧流转体系。
应用区块链技术建立社区虚拟币产生与流通机制,员工可通过发帖、提问、回答等行为的发生自动赚取虚拟币,并可利用虚拟币购买社区学习资料与服务,从而激发社区成员的参与度,形成以虚拟币作为核心激励机制与衡量社区贡献度重要指标的集体智慧生成与流转生态。
区块链的分布式账本还可以生成观点进化网络,员工掌握的技能将分布存储在网络中,根据各个观点之间的语义联系生成可视化的知识网络图,员工可以在这个分布式账本上查看自己形成的知识能力体系,更方便于员工查缺补漏,探索学习未知的领域。
索尼称就已经开发了基于区块链的集中式现代账本以储存教育资料,通过网络共享,采用新的记录及评估学习方式。而在2016年2月,索尼其实已宣布采用区块链技术,应用于培训领域,并开发了能够实现开放式、安全的学术水平与进步记录的共享技术。
将区块链技术运用到培训上,还更方便HR在岗位匹配时根据相应的任职资格和技能要求查找合适的人。
员工档案管理
区块链技术在建立分布式系统中存储的精确记录方面非常有效。通过区块链平台,员工将能够建立由加密验证信息组成的专业档案:由学校验证的文凭和由雇主验证的工作经历。
在不久的将来,招聘经理将要求简历和包含经验证的区块链上的信息,以便他们不必浪费时间验证凭证。员工个人资料越强大,该个人就可以获得更多机会。就像雇主可以验证一个人在那里工作一样,他们可以验证可以添加到员工专业档案中的个人成就。
当一个人获得承认,而不是接受一个使用有限的证书时,他们将被永久和不可改变地证明区块链上的成就。他们将能够将其添加到他们的专业档案中,这可以反过来用来推动他们的职业生涯。
员工也将因建立专业档案而受益匪浅。当他们完成培训计划,获得认证或从事慈善活动时,可以通过其雇主在区块链上进行验证,并使用该验证创建更强大的专业资料。
过去的成就不会被遗忘,并将具有实际的持久价值。这种认可对于员工而言实际上是真实的使用,并且将成为更大的动力来源。当雇佣公司开始寻找经过验证的成就而不是简历中未经证实的索赔清单时,员工将有更大的动力为其组织发挥真正的影响力,这也让区块链间接实现了激励员工的效果。
除了这些外,区块链在薪资方面具有优势,特别是在国际支付方面。 通过区块链的安全结构,可以实时向员工付款,可以成为企业向海外汇款的更便宜和更高效的方式。 比如澳大利亚公司Chronobank就是采用区块链技术让雇主无需通过银行就可以支付合同工。
-
 观点
观点
前谷歌员工变身CEO:OKR对我有多重要
编译| 姚琼
来源| HRCouncil
让我们一起来倾听一下前谷歌员工,现在是创业公司CEO是如何运用OKR来管理公司的。
从Google学到的目标设定系统
Karl Sun, LUCID CEO
Goal,是目标,而不是进球。目标很难,尤其是去设定雄心勃勃的目标。
偷窃伟大的思想,不是一种罪恶。
在Google成立的第一年,投资者约翰·杜尔提出了使用目标和关键结果法(OKR)设定目标的想法。他把它作为一种有效的方法,既能设定高水平的目标,又能以量化的方式衡量这些目标的进展。我确信他做了一个很有说服力的演讲,因为OKR很快就被整个公司接纳了。
OKR系统是在组织内设定可衡量的目标并将公司、团队和个人目标联结起来的有效方式。它使你的公司和员工在聚焦于一个明确、共同的目标,并不断发展壮大。
今天,每一个Google的新员工,在他加入的首周,都需要花时间观看Google的风险投资伙伴Rick Klau在YouTube上关于OKR的演讲与介绍。
当我离开Google创立LUCID软件的时候,我带来了OKR。因为我曾经用过,而且在Google非常成功。我坚信在LUCID同样会带来很多帮助,而且这套系统还没有让我失望过。
OKR的效益
1.设定远大目标
OKR为公司设定个人、团队和组织层面的目标建立了清晰、简单的模式。当你写一个OKR时,你先确定一个目标并在沙地上画一条线。在一天结束的时候,你可以用这条线来衡量自己,以确定你是否成功。相反,如果不事先设定目标,你就要努力证明你是否取得成功。
在Google,我们经常提醒自己,OKR是专门设计来推动你前进,而不是让你看起来不错。换句话说:目标应该很难,而不是扣篮。积极地去设定目标。
2.提高责任意识
在Google,我们所有的OKR都是公开的。我们在LUCID也是这样,让每个员工上传他们的个人OKR到我们的内部网络。这样做有助于提高责任意识和透明度,而且让目标再一次确认。当只有你一个人知道目标的时候,目标很容易被忘记。但是当有其他人(有时成百上千人)知道你的目标时,你就必然要承担其责任。
除了OKR的公开特点,每季度评分也有助于提高责任意识。Google使用0到1的刻度。你不应该用完美的分数来粉碎它。这些都是远大目标,所以如果你得到0.6到0.7,你就取得了很大的进步。事实上,如果你很容易达到你所有的OKR,那么你要么是超级英雄要么目标很低。
然而,重要的是要经常回顾并分析为什么你会落后于OKR,尤其是如果你的分数低于0.4。即使生病,或者优先级发生改变,但是你一定要诚实的找出根本原因。
3.保持组织统一
建立OKR,帮助公司中的每个人调整他们的目标。它使您能够确定精力聚焦在那里,以使公司目标统一。OKR是确保每个人都朝着相同方向共同努力的一种简单方式。并且,您可以检查所有运作,都联结和支持公司整体目标。
今年,我设定了一个目标“检查每个员工的个人OKR”,这大约有150个。虽然,我意识到会有很多目标和关键结果,但是我也意识到理解每个人的焦点所带来的价值。随着公司的不断发展,我与整个组织保持联系和了解每个人的工作方式是有限的。回顾OKR是一个很好的方式,看看其他人发现什么重要的举措,并评估如何符合我觉得重要的倡议。
让我们从设定OKR开始
建立OKR是非常简单明了的,这就是它的优点。
以下是一些基本的指导原则:
设置年度公司OKR,作为年度公司的规划。同时,也设定每个季度的OKR。年度OKR可能会调整,但季度OKR不应该变化。
部门基于公司OKR设定部门OKR。然后根据公司OKR和部门OKR设定个人的OKR。
下面是如何写一个OKR:
1.设定目标:目标告诉你要去哪里。每季度最多只能二到五个目标,这样你就不会把自己弄得精力分散。
2.为每个目标设置关键结果:关键的结果表明你将如何达到你的目标。关键的结果必须是可衡量的,换句话说,它们应该是可量化的。具体的目标应该在写在前面,并试着为每个目标设定最多不超过四个关键结果。
3.把你的OKRs储存在公共空间里。例如,Google把每个员工的OKR放在员工目录中。
4.召开1对1会议,回顾季度OKR进展。召开季度公司会议,回顾公司和团队OKR。
5.在每季度开始时,对前一季度的OKR进行评分。使用0到1的刻度,关键结果单独评分,目标的评分是其关键结果的平均值。不要使用OKR评分来进行员工评价。记住,如果你一直得分1,你的OKR就不够有挑战性。
从一个CEO的角度出发
记住,危机永远存在取得成功时。设置低门槛可能会让你的员工暂时感觉良好,但这并不能推动组织向前发展。我开始意识到,对于一个规模庞大的公司来说,我们都需要对自己正在做的事情感到不安,以便让我们持续取得成功。
我也强调了写你自己的OKR的重要性。即使你觉得你的OKR是公司OKR,明确定义,可以当作你自己工作的指南。作为CEO,在一个无底洞的任务中忙乱是很容易的,OKR可以帮助我专注于我应该做的事情。这样做也有助于展示你对OKR的承诺。
最后,你可以为自己或公司设置OKR,并意识到有些地方并不像你原先想象的那么重要。你并不需要被你的OKR锁死,你也可以调整你的方向。但是,你需要诚实的告诉自己,为什么你没有达成OKR。
谢谢,Google!在LUCID,我们不打算将OKR归还给Google。不仅它发挥了关键作用,让我们走上一个快速成功的轨道,而且它带来了坦诚!
让人怀念的OKR
Falon Fatemi,Node CEO
有时候,我们需要花时间理解一段经历教会我们的东西。
在2011年,我觉得我为我的创业冒险做好了准备。我学习了在线销售艺术,涉足Google的非盈利机构,致力于YouTube战略合作伙伴建设,甚至影响Google的全球扩张战略。
但回过头来看,Google教给我的东西比我当时意识到的要多得多。例如,我学会了处理拒绝和寻求导师。当我与早期公司合作并最终开始自己的业务时,我意识到了Google的一个工具的重要性:OKR。
OKR方法论
Google在创业的第一年,就推出了OKR(目标和关键结果)跟踪其目标的进展,有些目标持续了几年,而另一些则在每个季度发生变化。
即使在今天,Google也在公司、部门和个人层面上使用OKR来设定目标进度。大家通过观看Google的风险投资者Rick Klau演讲和介绍录像,可以很好地理解OKR是如何工作的。
我很怀念Google的OKR。在我的四年工作中,我使用这个系统来监控我自己的成长以及我的部门对Google的贡献。我甚至没有意识到,OKR在我身上根深蒂固,这是我工作的一个重要部分。
OKR在Node
当我创建Node时,我想到了我的目标。我们怎么知道什么时候雇佣第一个开发人员呢?我们什么时候寻求第一轮融资?这些问题使我想起了OKR。
我们最早的OKR是以产品为中心的。我们起草了一个时间表(发布、设定初步市场、规划产品的市场适应性)。今天,OKR帮助我们将公司的年度目标分为季度目标和部门目标。
OKR的基本原则是,它们是可衡量的。例如,销售OKR可能会在季度内达到一定的收入目标。营销人员可能会为合格的销售线索制定一个标准,而人力资源可以计划在本季度内雇佣特定数量的工程师。
随着你的公司增长到20人,OKR应该变得更加个性化。每个销售人员如何为公司的目标做出贡献,最终实现公司的成功?在这一点上,仅仅按部门创建OKR已经不再足够了,每个人都要有自己的OKR。OK,开始设定你的OKR。
如果你是一个创业公司的CEO,公司的OKR就由你负责。但是,当你带上部门负责人时,那些人应该负责起草团队OKR。
然而,有三个关键的错误要避免:
1.设定不合理的期望
做得好,OKR会给你的团队挑战性的目标,并明确地联结到公司的目标。但是,如果你让他们太过于脱离实际,就会失去信心,会挫败员工。平衡远大目标、可用资源和员工能力,这需要一点点的练习。基本上,你希望员工接近他们的目标,但不一定每次都击中他们。
2.跳过检查
没有定期的评估,OKR就失去了意义。把季度检查看作要遵守的合同。为了帮助他们坚持目标,让他们公开OKR。这样,每个人都可以看到其他人在做什么,他们在做什么。Google员工可以从员工outlook中查找任何一位现任和前任OKR,目标从CEO拉里·佩奇那里分解下来。
在Node,我们每月和季度检查OKR。作为CEO,我的职责是与各部门负责人面谈,以确保员工的目标与公司目标一致。我也有责任通过每月对公司的OKR进行公开的评估来塑造良好的习惯。
3.不庆祝OKR成功
OKR是很好的管理工具。但是当你不庆祝胜利的时候,你错过了认可员工辛勤工作的机会。对于年轻的创业企业来说,就实现商业目标而言,关键在于建立一支紧密团结的团队。
Node正在创建一个语境网络,我们需要有动力的、有激情的员工来帮助我们。通过花时间来庆祝这些里程碑,我们创造了需要达成雄心勃勃目标的友谊。
如果OKR听起来简单,那是因为它们本身就简单,这就是它的价值所在。他们帮助公司,无论是Google一样的巨头还是小型创业公司,把大的目标分解成小的、艰巨但可行的任务。OKR帮助你成为你想成为的公司。记住,每季度开展一次。
-
 观点
观点
人力资源岗位都要进行哪些数据分析?
作者|刘建华
来源|HRBar
在HR的绩效考核里经常性会看到一些指标,比如招聘的到达率、培训完成率等,到底人力资源要分析哪些指标,这些指标到底如何设计?
01
基于运营的人力资源数据分析
首先第一个核心点,如果HR在操作人力资源工作的时候没有数据化没有进行量化,那么操作的东西就很难获得认可。
量化是今天所有HR的基础,特别是各位写年度工作计划和总结时,一定要量化很清楚。
第二是到底量化什么指标,很多HR在做半年度分析的时候,部门人员占比,再分析工作人员结构占比、年龄占比,我个人认为这个东西意义并不大,真正来分析的是基于公司运营数据导出来人力资源分析,这个是最有意义的。
人效分析、各个岗位单位产出分析、人力成本分析、牛人占比分析、培训有效性分析,这些都是我认为比较有意义的数据。
02
人效分析
第一个数据是人效分析,在一个公司里这是最基本的数据,因为人效分析就知道公司目前经营情况,人效的公式比较简单,用公司收入除以人数,每个月加起来除以12个月。是按照人均收入还是人均毛利来算,我个人认为按收入分析就可以,人效的比值决定了公司里每个人的平均贡献值。
第一种情况,是公司的产值偏低,同样1000人能创造十亿的收入,公司只做了一亿的收入,产值为什么比较低?仔细分析会发现产品比较低端,就是卖不上价格,这样的公司肯定是产品线的产品水平不行。
第二种是人员能力不够,一般公司里人效值偏低的时候,往往是公司初级人员偏多,导致整个公司战斗力不行,产值上不去。
第三种是,有些公司的产品线也赚钱,但做得不太好,原因是公司有一堆不赚钱的业务,所以我个人认为要控制业务数量,按照谷歌的思想就是721,70%做主营业务,20%做成长型业务,10%做新业务,这样的占比就比较健康,所以要控制一个合理的度。
03
人力成本分析
下一个分析是人力成本的占比,这跟人效比密切相关,往往是一个公司人力成本除以公司财务确认后的收入。
人力成本分析怎么算呢?一般是,人力成本占收入是一个比,还有收入占毛利的比,我认为占20%左右比例合适。
有很多人说人力成本控制的方式是什么,一些公司的玩法就是不涨工资,我认为这是不可取的,控制人力成本有一个核心动作是必须减员增效。
在公司里哪些人浪费人力成本呢?
第一就是无能的高管,第二就是工资很低但没有产值的人。
降低人力成本一种办法是降低工资总额,还有一种办法是提高收入值,怎么提高?要找牛人进来,因为牛人可以做更高的收入,找牛人也是降低人力成本的好办法。
04
人员结构分析
第三个是人员结构的分析,这里指的不是年龄、性别、学历分析,这种盘点价值并不高,那什么样的分析才有意义?
第一个分析的是公司管理人员占比。
第二是后台人员的占比分析,财务、人力资源等等岗位,你问这些岗位是不是越少越好?不是。我个人觉得一个公司后台加起来维持在12-15%是可以的。
还有一个是公司里人员结构,比如研发人员占比分析,之前的课我们讲过,华为46%的人是做产品和解决方案的,在中国的3G根本没有想商业化的时候,2004年的时候华为就开始招人,当时3G人才有1万人左右,有7000人在华为,他们的研发储备量比特别高。
05
营销团队能力水平分析
下一个分析是对营销人员产出进行分析,第一个是组织单元的分析,我要看各个门店的产出情况,看看各个门店人均产出多少钱,看看各公司的人效比是什么样的。
第二是分析销售人员的业绩情况,做这个分析核心点是有了这个之后,在公司里把销售人员按照业绩进行排名,然后按照等级分出来。
要认真剖析整个公司的人员构成,你要看各个业务部门做得最好的人是多少,前1/3的人做多少,把后1/3的人干掉,中间1/3是可以培养的人,在销售里这个分析特别重要,必须要对这个人的水平进行深度分析。
06
一定要做的人员综合能力满足预期业绩分析
在分析里最重要的是,分析公司现有员工满足未来预期业绩要求的匹配度分析。
把下半年的目标定出来,基于未来业务的要求,现有人员是不是满足这样的要求,要把人员进行分类分级,就是前面讲的人力资源盘点,里面包括最基本的个人业务能力评估、态度盘点、个人价值观匹配、个人发展潜质匹配等等。
这样在公司就会分出三类人员。
一类是表现很好业绩过关而且潜质不错,完全胜任岗位要求;
第二类是勉强可以的人,业绩中等一般但是也可以达到及格线;
第三类是根本达不到要求的人。更深层次的分析,老板最希望看到的分析是这个,在一个公司内部到底有多少人是真正胜任的,他们是能够满足公司业绩要求的。
最牛的人力资源是对每个部门的每个人都很熟,对他们实际情况都很清楚,这样人力资源就干得比较狠了。
各个部门的人员匹配都比较清楚,哪个部门行与不行都很清楚,下一步怎么调也很清楚,作为HR来说,能不能对公司各个部门的人员了如指掌很重要,是不是对每个业务部门下一步工作目标业务计划了如指掌。
07
从运营角度进行招聘分析
下一个分析是专项数据分析,比如招聘渠道的分析,这个怎么分析?
原来分析数据的时候是招聘到岗率,要看招聘完到岗后的分析,如今招的人不仅是简单把人招进来,而是要确定他是牛人。
今年部门招了多少人,到岗周期时间要进行分析,然后针对招聘结果进行分析,是不是满足岗位要求,部门提了多少需求,HR多少天搞定的,招来的人转正通过率有多少,转正的优秀率有多少,这样剖析之后招聘的数据就比较有说服力。
有很多HR总是掉在模块思维中来做,分析的时候先分析招聘渠道完成情况,通知了多少人,多少人来面试,通过率有多少,这些数据一点意义没有,一百个人招进来录取了一个人,招聘了一个人录取了一个人,哪个更重要呢?我认为通知一个人就可以招聘上岗,这是最好的。
08
分类细分的流失率分析
关于员工流失率的分析,并不应是简单算一个流失率。
第一个数据是主动淘汰人员的数据,做这个目的是我们能非常清楚的知道主动淘汰了多少人,这是一个很核心的数据。
第二个是主动流失员工有多少,比如说要看那些主动流失(主动离职)的人有多少。
在这里要进行精细分析,什么叫精细分析?一个是优秀员工牛人的流失率分析,这个比值一定要控制好,如果这个没控制好的话特别可怕,一个公司里牛人走了,这个组织损失就大了。
我建议要立体性的进行分析,就是统一的流失率,从主动和被动流失率进行分析,再看牛人流失率。
其实这些数最后要体现到人效提升上,不管你怎么做,招了多少人进来,走了多少人,分析数据的优势是引进了多少牛人,干掉了多少不行的人,这样工作才有效,反过来说招了很多人没有效果,牛人还走了,这样人力资源的工作就有问题了。
09
培训分析与总结
最后一个是对培训数据分析,第一个是课程开发数量,今年我们有多少个经过准确认真开发课程的数量;第二个是我们经过认证的内部讲师有多少个;第三个是当年做了哪些有效培训。
针对于公司不同的岗位,把这些工作——量化后进行剖析,发现培训完之后团队业绩明显有增长,培训前后的数据比一分析,有了这个值就厉害了,人力资源的价值感就上来了。
做了这么多分析最后总结下来是什么?
第一个是体现跟运营的对接;第二个是跟HR的贡献值有关系,你能拉出来人力资源贡献了什么,今年人效有提升,薪酬成本降低,牛人招聘入职率高,牛人流失率低,培训了多少牛人出来,这时候HR获得重用的机会就来了。
必须要用数据化分析,你得用数字证明你的功劳,否则只有苦劳没功劳,干了半天最后也是白干。
-
 观点
观点
新型人才管理模式“海盗指标”改变HR的工作方式
来源| digital hr tech
文| Erik van Vulpen
包括我们在内的很多人都在寻找有效的人才管理模式,但到目前为止还没有人开发出这样的模式。因此,本文介绍了一种人才管理模式,您可以使用它来充分发挥员工的能力。
AARRR模型
很多年前,我就在教大学生创业。我最喜欢解释创业营销的模型之一是海盗 - 或AARRR模型(最初由Ash Maura提供)。我通常会问:“海盗吸什么烟?cigAARRR!”
(注:cigar是雪茄的英文拼写。这里是谐音。)
AARRR模型首先显示顾客如何与组织联系,并最终从该组织购买某物。一共分为
五个阶段。
获取:首先要驱使顾客拜访公司。
激活:组织和客户之间交换的第一个价值体验。例如,客户留下他们的电子邮件地址以换取每月的新闻。
收入:也是最重要的部分。收入就是让客户做出购买决定。不用说,这是公司的生命线。
推荐:你如何让客户告诉他人关于你的信息,以便你获得更多客户?
保留:你如何保留那些有过购买记录的顾客,以便他们回来再购买?
当然,现在我可以告诉你这种模式的有用程度以及如何使用不同的媒体渠道来获取和激活客户,鼓励他们做出购买决定等等。
然而,最大的问题是:我们如何将这个模型应用于人力资源?
人才管理模式
当我们需要创建人才管理模式时,我刚刚描述的营销模式就是一个完美的模板。通过与客户完全相同的流程来服务员工。
另外,运用类似模式工作有助于将员工视为“内部顾客”。将员工视为客户有助于我们推动客户或提供卓越的服越。这是人力资源部门仍然可以从销售和营销等相关学科中学到很多东西的领域。
所以,让我们开始吧。首先,这里是人力资源的人才管理模式:
现在,让我引导你了解每位员工在此人才管理模式中所经历的5个步骤。
获取:获取就是吸引潜在的候选人到您的组织。在招聘领域,这被称为雇主品牌。
你如何理解这个词并让人们认识你?
你将如何成为人们想要为之工作的吸引人的雇主?
你如何确保你的公司是平易近人的,这样你就可以将认识你的人变成想要申请你的公司职位的人?
这些都是基本的问题,当你认真成为一个更好的雇主时,你需要能够回答这些问题。
激活:激活是关于选择候选人,候选人体验和让候选人上道这三件事。
你将如何从人才库中选择合适的人才?
你如何做出正确的选择以避免雇佣不良员工?
你如何将候选人变成大使?你如何确保你的候选人体验接近完美?
你如何拒绝候选人,但仍然给予他们最好的体验,并与他们保持联系以进行其他工作?
你如何让你的员工融入公司,让他们留在你的公司,并提高生产力?
这些问题可以确保你聘请到市场上最优秀的人 - 而且让你决定不雇用的人回家时感觉很好。
收入:收入是关于充分发挥员工的能力。这包括入门,学习和开发以及绩效管理等主题。
你如何确保人们更快地上道?
你将如何减少你的新员工的全部生产力?
你将如何确保你的员工保持竞争力并在未来继续保持业绩?
你将如何保持你的员工参与?
你如何确保人们通过有效的绩效管理来充分发挥他们的能力?
推荐:推荐是关于让新人进入和建立你的声誉。这可以吸引新员工或利用员工来扩大客户群。
我们如何创建一个有效的员工推荐计划?
我们如何让我们的员工拥护我们的品牌?
我们如何利用我们的员工扩大我们的客户群?
员工推荐计划非常流行。通常被推荐的员工效率更高,表现更好,不太可能过早离开。
保留:就像你想留住你的客户,你想留住你的员工。如果你的人才认为你的组织不适合工作,那么你就有一个大问题。主题包括保留,幸福,补偿和福利。
你将如何减少自愿离职率?
你将如何补偿你的员工以确保他们快乐?当然,补偿并不总是财务方面的。非财务激励措施也同样适用。
你将如何使用可变薪酬来确保你的销售人员表现最佳?
你将如何确保你的组织保持作为一个好工作场所的声誉?
保留是关于尽一切努力保持最佳表现者。
此外,良好的保留策略 - 以及人才管理指标的使用 - 有助于建立竞争优势。如果你最好的员工永远不会离开,你将超越你的竞争对手。
正如您所看到的,人力资源人才管理模式有助于构建和优化您的所有人才活动。
人力资源人才管理模式的实践
好的,现在我们来看一些例子。
获取和保留:雇主品牌和奖励在Pret a Manger
我不知道你是否曾经在Pret a Manger找过一杯咖啡或一份健康的零食,但如果有的话,你会知道我在说什么。每当你进入Pret商店,十分之九的员工都会真诚友善,笑脸而不会是假笑。
那可能是对的吗?我在问自己同样的问题。
当然,这里有几个因素起作用。其中之一就是他们在Pret有这样一条规则:无论何时一个客户让员工笑起来 - 只是希望他们有一个愉快的一天,或者开一个友好的笑话 - 员工可以给客户一个免费赠品。结果?顾客开心,员工开心,生意开心。
另一个重要因素是,根据以往的经验,Pret不会根据以往的经验进行聘用,而是根据(其中包括)候选人是否符合公司核心行为:激情,清晰谈话和团队合作。 Pret a Manger这样一位有吸引力的雇主的所有良好范例。
除了吸引员工之外,Pret的做法也直接影响公司的留用率:年营业额从90%下降到2015年的60%(这对于Pret来说是一个非常稳固的数字),而且80 Pret a Manger公司的经理人开始以团队成员身份出现。
激活:选择,候选人体验和在Dignity Health的入职
Dignity Health在Glassdoor 2017年“美国访谈最佳五大名单”排行榜中名列第一。当被问及你如何建立一个优秀的候选人体验时,Dignity Health人才招聘总监Kristie Griffin提到了以下内容:
为候选人准备
重视价值和技能
标准化价值评估
让候选人放心
前五名的其他公司提到了诸如要求面试官分享他们的个人经历,让候选人知道他们的立场,并为面试官制定指南。人才激活的所有优秀例子都做对了。
收入:Google的学习与发展和绩效管理
谷歌是一家经营绩效管理的经典案例,它的成效与众不同。该公司专注于员工目标设定而非正式排名。 Google员工设置了自己的所谓客观和关键结果(OKR),管理人员试图指导员工创建和实现目标。这可以帮助员工实现这些目标,从而帮助组织更有效地实现其公司目标。
人才管理模式有助于映射员工之旅,是以员工为中心的人力资源管理的典范。你能将你的组织映射到这个人才管理模型上吗?
 扫一扫 加微信
hrtechchina
扫一扫 加微信
hrtechchina
 观点
观点
 观点
观点
 观点
观点
 观点
观点
 观点
观点
 观点
观点
 观点
观点
 观点
观点
 观点
观点
 观点
观点



 扫一扫 加微信
hrtechchina
扫一扫 加微信
hrtechchina




